
Unified Data Management (UDM)
The Network Exposure Function (NEF) is a key architectural component within the 5G (Fifth Generation) mobile network infrastructure. It plays a crucial role in enabling external applications and services to access and interact with the 5G network, allowing for innovative and customized service offerings. The NEF is part of the 5G Service-Based Architecture (SBA) and contributes to the openness and flexibility of the 5G ecosystem. Here’s a detailed description of NEF and its functions:
- Network Exposure and API Management: The NEF primarily facilitates network exposure to external applications and services through well-defined Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). These APIs provide a standardized and controlled way for third-party developers to access specific functionalities and data within the 5G network.
- Policy-Driven Access Control: NEF enforces policy-driven access control to ensure that only authorized applications and services can access the network and utilize its resources. Policies define the rules and conditions under which external entities can interact with the network, including permissions, data access rights, and usage restrictions.
- Subscriber and Context Information Exposure: NEF allows external applications to access subscriber-related information and contextual data. This might include user profiles, preferences, location data, network capabilities, and other relevant context that can be leveraged to deliver personalized services and enhance user experiences.
- Security Functions: UDM plays a vital role in ensuring the security of user data and network communications. It manages the generation and distribution of security keys and other security-related parameters to secure communication between the user equipment (UE) and the network.
- Profile Management: UDM manages user profiles, allowing customization of services and resource allocations based on individual user preferences, service requirements, and network conditions. It ensures that each user receives a tailored and optimized experience.
- Interactions with Other Functions: UDM interacts with various other network functions, such as the Authentication Server Function (AUSF), Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF), and Network Slice Selection Function (NSSF), to provide a seamless user experience and support essential network functions.
- User and Application Interaction: UDM enables interactions between users and applications, allowing for personalized and context-aware service provisioning. It helps in mapping applications to users based on their preferences and profiles.
- Integration with Policy Control: UDM integrates with the Policy Control Function (PCF) to provide policy information related to user QoS, traffic management, and other policy decisions. This integration helps in efficient policy enforcement within the network.
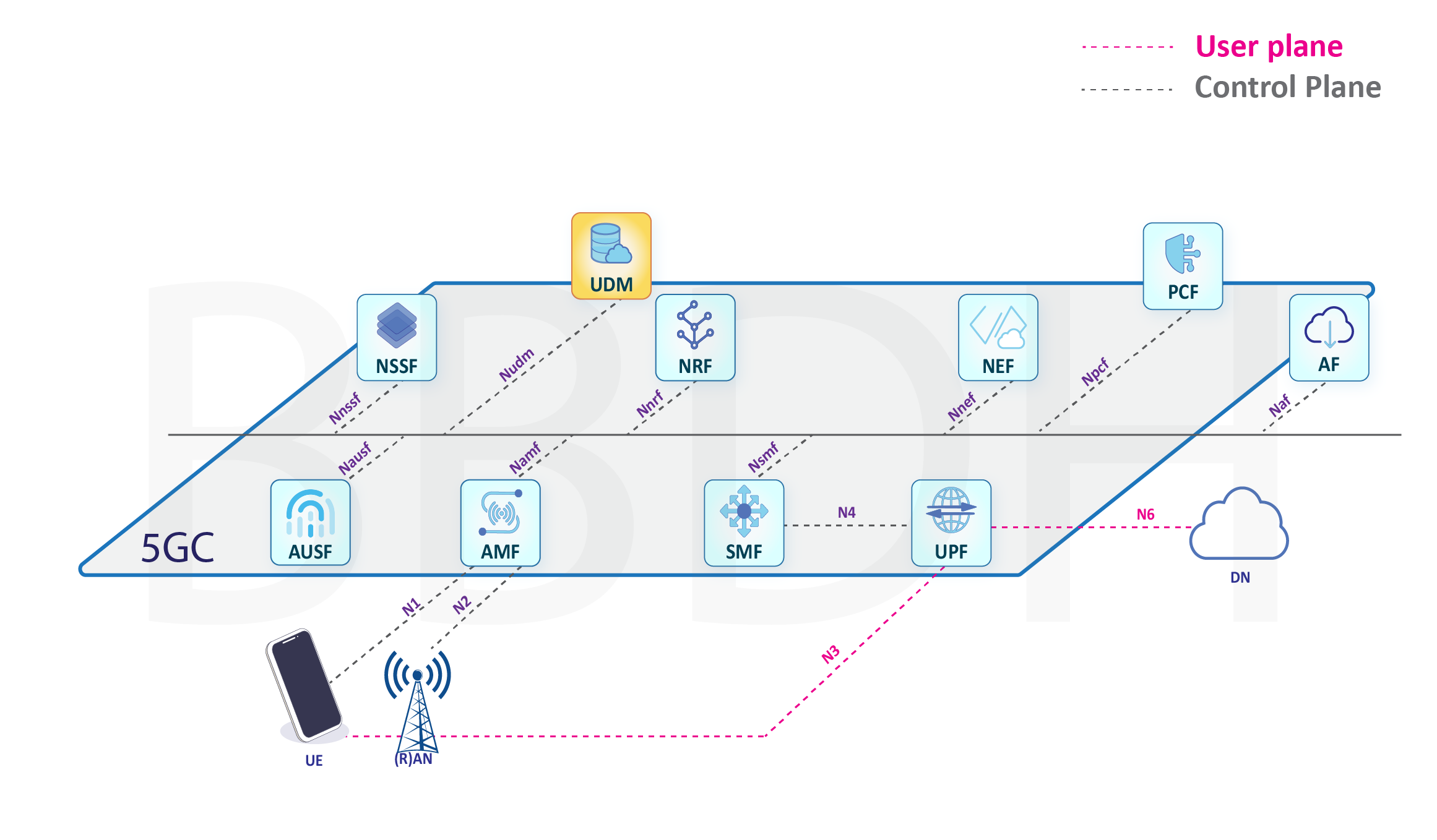
In summary, Unified Data Management (UDM) is a critical element in the 5G Core architecture, serving as the centralized repository for user-related data and authentication information. It plays a vital role in managing subscriber data, authentication, authorization, and enabling personalized services and security within the 5G network.

 Search
Search