
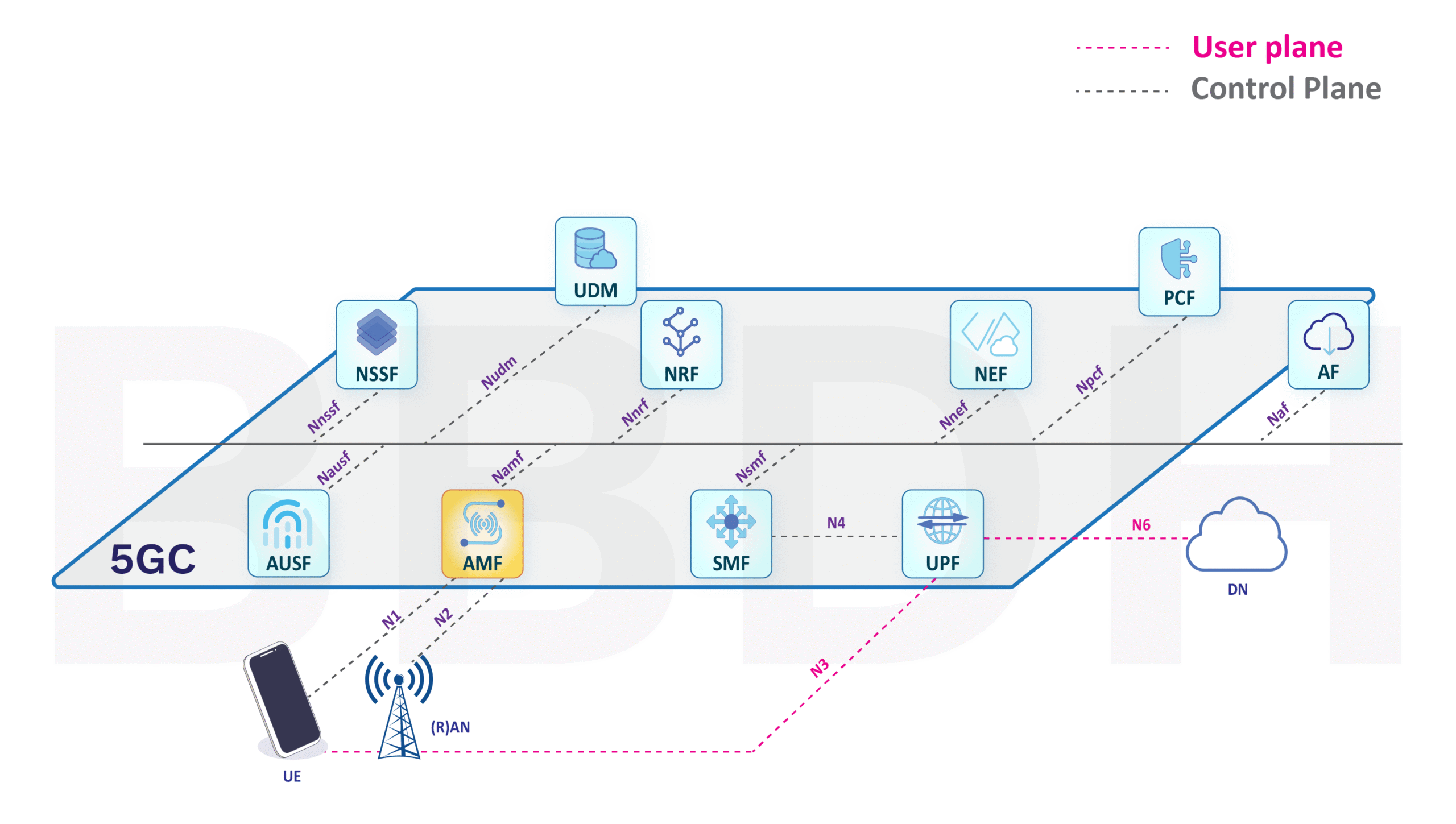
Access & Mobility Management (AMF)
AMF, or Access and Mobility Management Function, is a fundamental network function within the 5G Core (5GC) architecture. It plays a crucial role in managing and controlling access to the 5G network for user equipment (UE) and ensuring seamless mobility of the devices within the network. Here’s a detailed description of AMF and its functions:
-
- Access Control: AMF is responsible for controlling and managing access to the 5G network. It authenticates and authorizes the User Equipment (UE) trying to connect to the network, ensuring that only authorized devices gain access.
- Mobility Management: AMF facilitates mobility management for UEs, ensuring that the devices can move seamlessly within the network while maintaining continuous connectivity. This includes handling procedures related to handovers between different access points or networks.
- Security Functions: AMF implements security functions to ensure a secure connection between the UE and the network. It manages security key handling, encryption, and authentication procedures to protect data transmission and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of information.
- User Authentication and Authorization: AMF authenticates and authorizes users, validating their credentials and ensuring they have the necessary permissions to access the network and its services.
-
- Registration and Deregistration: AMF manages the registration and deregistration processes for UEs in the network. When a UE connects to the network, AMF facilitates the registration, allocating necessary resources and setting up necessary connections. When the UE disconnects, it handles the deregistration process.
- Session Management: AMF assists in session management by establishing and managing communication sessions for UEs. It coordinates with other network functions like SMF (Session Management Function) to set up and manage these sessions efficiently.
- QoS (Quality of Service) Enforcement: AMF enforces QoS policies, ensuring that the required level of service quality is maintained for different types of traffic and applications. It coordinates with other network functions to guarantee that QoS requirements are met.
- Policy Interaction: AMF interacts with the PCF (Policy Control Function) to make policy decisions related to access, mobility, and QoS. It ensures that policies defined by PCF are appropriately applied and enforced throughout the network.
- Integration with Other Network Functions: AMF collaborates with various network functions within the 5G Core, such as SMF (Session Management Function), UPF (User Plane Function), and PCF (Policy Control Function), to ensure smooth access management, mobility, and service delivery. In summary, the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) is a vital component of the 5G Core architecture, responsible for controlling access to the network, managing mobility, enforcing security measures, and ensuring the quality and continuity of communication services for user equipment within a 5G network.
In summary, the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) is a vital component of the 5G Core architecture, responsible for controlling access to the network, managing mobility, enforcing security measures, and ensuring the quality and continuity of communication services for user equipment within a 5G network.

 Search
Search